
Web3
Augmented Reality: Introduction

The fabric of reality is changing! But, not in the way that I expected when I was watching sci-fi shows as a kid. Rather than upsetting reality — we’re augmenting it.
Augmented reality is a major initiative here at Scalio. The possibilities run the gamut from commercial sales to surgery. The market report is quite promising as well, predicting that the augmented reality market size will reach 89$ billion by 2026 - a CAGR of 46.3%. That’s right up there with the most promising industries in the world.
In this series of blogs on augmented reality, we’ll be covering some of the most exciting uses of augmented reality (AR) and answering the fundamental questions surrounding the topic. In this entry specifically, we’ll explore two main questions — what is augmented reality and what is augmented reality used for?
What is Augmented Reality?
Before we get too deep into it, let’s cover the basics of AR. AR is a technology that allows us to add to, or augment, waking reality. This is often done using a digital overlay.
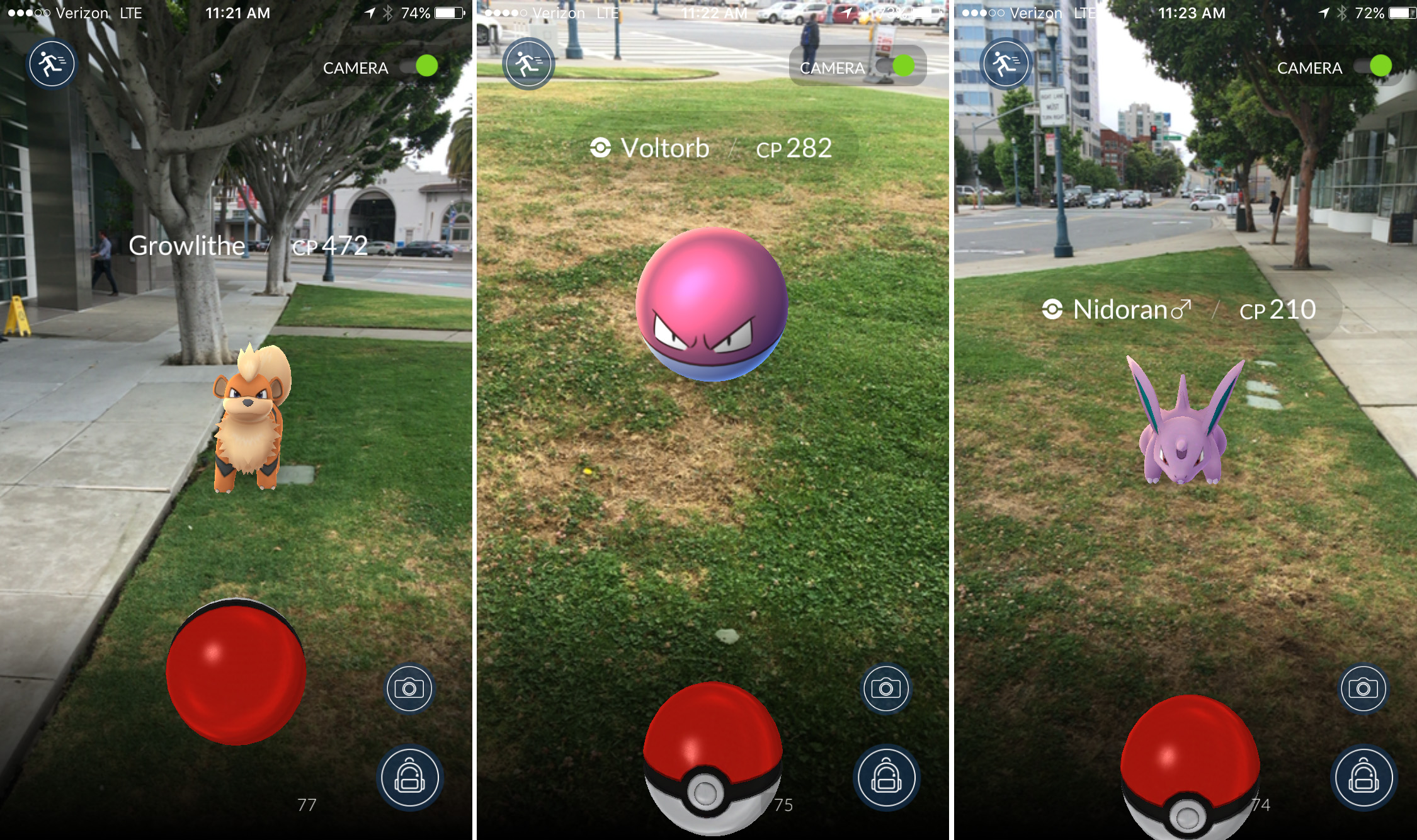
For example, Pokemon Go! uses smartphones to add digital information to reality through the phone’s camera. When players look through the Pokemon Go! app, they see computer-generated information in the form of an overlay on their smartphone. Almost every smartphone is capable of producing an AR experience. Because of the abundance of smartphones, AR technology is extremely promising.
Don’t get augmented reality confused with virtual reality. You've probably heard of virtual reality too, which isn’t the same thing. Virtual reality creates a brand new reality. Computers generate an environment complete with objects and scenery that feel immersive to the user. This can be anything from a video game on Xbox to an Oculus Rift.
They can sound similar, but the technologies and applications are quite different so we keep the concepts of AR and VR separate.
AR in Games
Augmented reality brings new interactive possibilities to gaming. Digital overlays make it possible for almost any gaming universe to be projected onto reality. We’ve mentioned Pokemon Go!, but it isn’t the only AR game out there. You can play as a medieval knight in Knightfall, run from zombies in Zombie, Run!, or hone your wizardry in Harry Potter: Wizards Unite. Pick your favorite genre, download the game, and live out your fantasies.
The AR gaming market had a value of about 4.7 billion dollars in 2020 and may rise as high as 28.60 billion dollars by 2026 according to BusinessWire. A few factors account for this high growth prediction. First of all, the gaming industry is already growing at a rapid rate. Secondly, AR games can be accessed on almost any smartphone, and in the future, as smartphone technology develops, AR games will become more interactive, visually pleasing, and fun. AR games are still in a nascent phase, but with the rise of play-to-earn games and NFTs in games (check out our blog), we can expect some serious growth in the near future.
AR in Art
Make no mistake, augmented reality doesn’t only exist in games. AR opens up a world of possibilities for artists as well. The burgeoning digital art community has blown up with the advent of NFTs, which provided a system of ownership for digital art. The concepts of AR and NFTs go hand in hand because up until now, NFTs in art have mostly existed in 2D. With AR, artists can add additional context to their art, creating brand new 3D experiences. Pieces of art can move, change size, and be displayed in any room of a house through smart devices. In this way, AR gives artists a world of artistic expression to work with. AR art is more of an experience than a traditional static piece of art.
AR in Health
Even though a lot of augmented reality’s usages are in a more commercial realm, we can’t overlook AR’s usefulness in healthcare. There are at least two major fields in which AR has been revolutionary. First, AR technology has made surgery more accurate and safe. During surgery, vision is often limited, especially if the operation is invasive. AR compensates for this lack of vision by using patient images and data to make surgeries more accurate. Not only that, but in serious cases, surgeons can coordinate virtually, delivering better care to patients when a surgeon isn’t available.
The second usage is the education of not only surgeons and doctors, but patients as well. AR allows medical professionals to communicate complex topics with the aid of images rather than words alone using AR technology. For educators, A detailed study of AR in medicine from Medical Education Online Educational found that AR-enabled education was especially useful during the Covid-19 crisis when students weren’t able to convene in person.
AR in E-Commerce
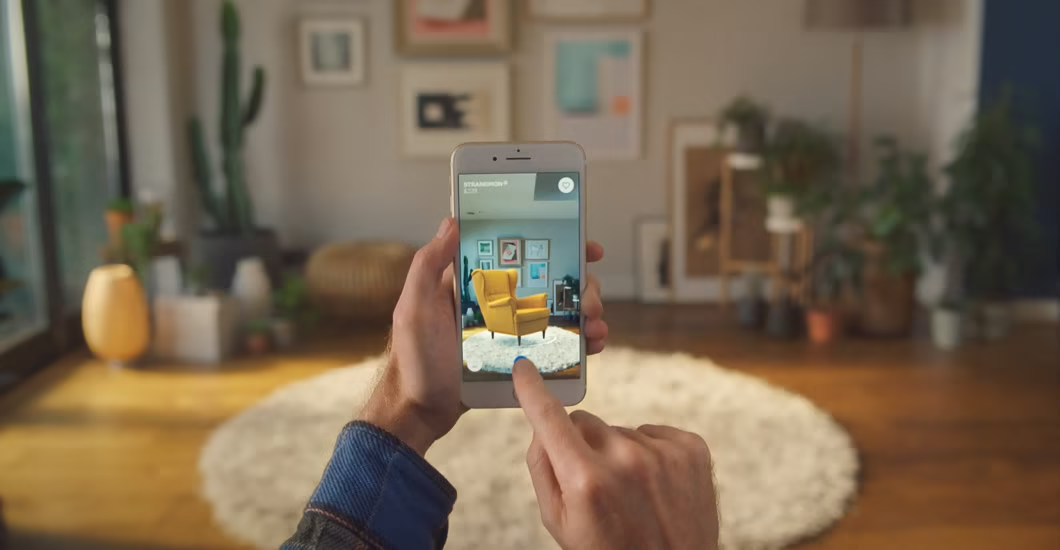
AR is making waves in traditional commerce as well, possibly even more than in art or games. Have you ever bought shoes from an online store only to find out that they didn’t look or fit at all like you thought they would? AR allows you to sample pieces of clothing, or anything that can be visualized, using AR technology — before buying.
In this photo, you can see Ikea’s new AR visualization app. Now, you can see how furniture will look anywhere in your home before you buy it.

Concluding Thoughts
We’ve covered some of the main industries where you’re likely to see AR. AR creates so many possibilities, that it’s likely to become a part of our daily lives. It requires only a smartphone with a camera from consumers, making it widely usable. Keep an eye out for more blogs on AR as we dive into the specifics of each of the topics mentioned above.



